Exhibit 17.8.A realtor wants to predict and compare the prices of homes in three neighboring locations.She considers the following linear models:
Model A: Price = β0 + β1Size + β2Age + ε,
Model B: Price = β0 + β1Size + β2Loc1 + β3Loc2 + ε,
Model C: Price = β0 + β1Size + β2Age + β3Loc1 + β4Loc2 + ε,
where,
Price = the price of a home (in $thousands),
Size = the square footage (in square feet),
Loc1 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 1,and 0 otherwise,
Loc2 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 2,and 0 otherwise.
After collecting data on 52 sales and applying regression,her findings were summarized in the following table. 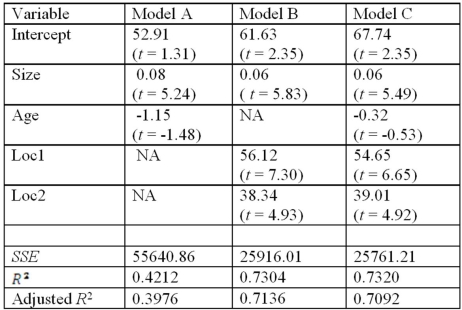 Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Refer to Exhibit 17.8.Using Model C,what is the null hypothesis for testing the joint significance of the two dummy variables?
Definitions:
Discretionary Product
A non-essential good or service purchased with disposable income, often subject to personal tastes and economic conditions.
Shopping Product
Goods that a consumer, in the process of selection and purchase, characteristically compares on such bases as suitability, quality, price, and style.
Convenience Product
A consumer item that is widely available and purchased frequently with minimal effort.
Unsought Product
A type of product that consumers typically do not think of buying until a need arises or they are made aware of it through advertising.
Q14: The returns to which of the following
Q19: For the model y = β<sub>0</sub> +
Q24: The standard error of the estimate measures<br>A)the
Q24: Exhibit 19-7.The following table shows the value
Q28: Consider the following simple linear regression model:
Q28: Exhibit 16.2.Typically,the sales volume declines with an
Q30: Exhibit 17.8.A realtor wants to predict and
Q38: Exhibit 15-1.An marketing analyst wants to examine
Q80: Exhibit 16-4.The following data shows the cooling
Q107: Exhibit 15-2.A sports analyst wants to exam