Exhibit 13.5 A police chief wants to determine if crime rates are different for four different areas of the city (East(1) ,West(2) ,North(3) ,and South(4) sides) ,and obtains data on the number of crimes per day in each area.The one-way ANOVA table and Tukey's confidence intervals are shown below. 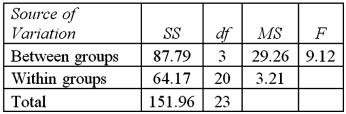
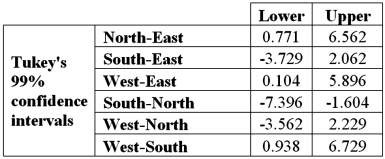 Refer to Exhibit 13.5.At the 1% significance level,the conclusion from Tukey's confidence intervals is:
Refer to Exhibit 13.5.At the 1% significance level,the conclusion from Tukey's confidence intervals is:
Definitions:
Confirmation Bias
A predisposition to identify, comprehend, prioritize, and recollect facts in ways that corroborate one’s existing beliefs or suppositions.
Overconfidence Bias
The tendency for an individual to overestimate their abilities, knowledge, or performance capabilities.
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it, often referred to as the "I-knew-it-all-along" effect.
Pragmatics
The branch of linguistics focused on the ways in which context contributes to meaning, including how speakers use and understand statements.
Q7: Two random samples are considered independent if
Q11: Exhibit 13.8 A market researcher is studying
Q20: Consider the following hypotheses that relate to
Q24: A simple linear regression,<img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2339/.jpg" alt="A simple
Q32: Consider the following regression results based on
Q50: In testing the difference between two population
Q63: Pfizer Inc.is the world's largest research-based pharmaceutical
Q80: Exhibit 10.13.A consumer magazine wants to figure
Q87: Exhibit 15-7.A manager at a local bank
Q95: Exhibit 15-8.A real estate analyst believes that