Use the figure to answer the question.
The figure represents the parabolic trajectory of a ball going from a to e in Earth gravity but without air resistance. The initial velocity of the ball is Vo at an angle 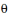 to the horizon. The vertical dashed lines represent equal time interval,
to the horizon. The vertical dashed lines represent equal time interval, 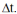
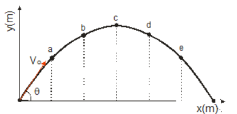
-The vertical velocity at point b is: Note: (g = 9.81 m/s2)
Definitions:
Accounting Methods
Systems and rules used for measuring, tracking, and recording a company’s financial transactions, often influencing how income and expenses are reported.
Common Size Statements
Financial statements that present all line items as a percentage of a base figure, facilitating comparison across time periods or companies.
Total Assets
The total of a company's assets, encompassing both current and long-term assets.
Cross-sectional Analysis
A type of analysis that examines data collected at a single point in time across multiple subjects, variables, or segments.
Q10: The London Eye, which is a giant
Q17: A mass M = 5.6 kg on
Q26: You walk 12 km south and then
Q48: The power developed by a certain engine
Q69: If you apply the same force to
Q86: The weight of an object is<br>A) the
Q99: You shoot an arrow with a mass
Q108: Write the statement in terms of
Q115: The resistance of a wire varies
Q178: A rectangular garden is surrounded by