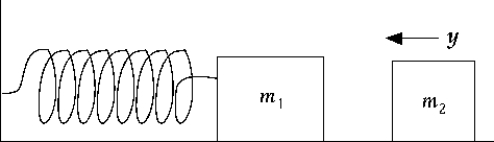
 A mass of 0.50 kg is attached to a massless spring with a spring constant k = 600 N/m (see figure above) . The system rests on a level, friction-free surface and is initially at rest. A second mass of 0.20 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with the mass attached to the spring; thereafter, the oscillating system vibrates with an amplitude of 0.25 m. What was the incident speed of the second mass?
A mass of 0.50 kg is attached to a massless spring with a spring constant k = 600 N/m (see figure above) . The system rests on a level, friction-free surface and is initially at rest. A second mass of 0.20 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with the mass attached to the spring; thereafter, the oscillating system vibrates with an amplitude of 0.25 m. What was the incident speed of the second mass?
Definitions:
Spectroscopic Technique
A method used to measure the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter, often to identify or quantify components within a sample.
Alcohol
A chemical compound that is organic in nature, identified by the presence of at least one hydroxyl group (-OH) linked to a carbon atom.
Splitting Tree
A graphical representation used in mathematics and computer science to describe the structure of an algorithm or a process that divides a problem into smaller parts recursively.
Trans
A descriptor in chemistry used to denote molecules where two substituents are on opposite sides of a double bond or a cycloalkane ring.
Q10: In the absence of air resistance,
Q17: The vector <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6080/.jpg" alt=" The
Q19: What is the angular frequency of oscillation?<br>A)
Q36: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6080/.jpg" alt=" A reversible heat
Q64: If it is known that two bodies
Q78: A particle moving in simple harmonic motion
Q80: The ratio of the fundamental frequency (first
Q88: A solid sphere of radius r
Q92: While you are standing on a corner,
Q99: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6080/.jpg" alt=" Near resonance, if