Present Value of 1 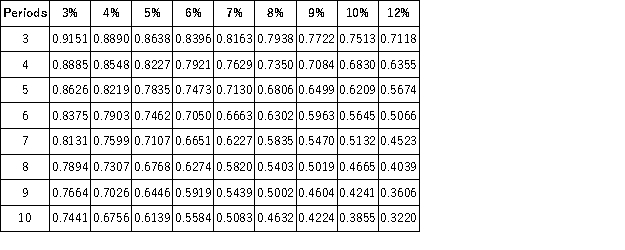 Future Value of 1
Future Value of 1 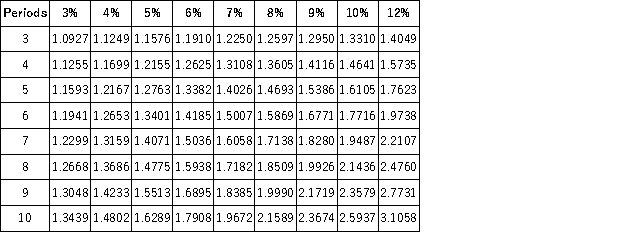 Present Value of an Annuity of 1
Present Value of an Annuity of 1 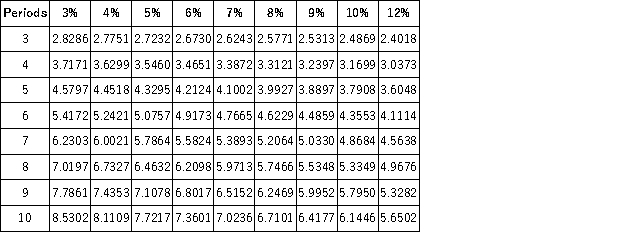 Future Value of an Annuity of 1
Future Value of an Annuity of 1 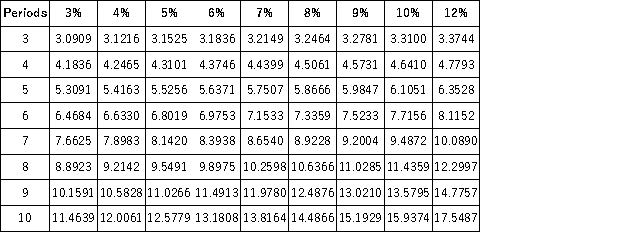 Trey has $105,000 now. He has a loan of $175,000 that he must pay at the end of 5 years. He can invest his $105,000 at 10% interest compounded semiannually. Will Trey have enough to pay his loan at the end of the 5 years? If not, by how much will he be short?
Trey has $105,000 now. He has a loan of $175,000 that he must pay at the end of 5 years. He can invest his $105,000 at 10% interest compounded semiannually. Will Trey have enough to pay his loan at the end of the 5 years? If not, by how much will he be short?
Definitions:
Employer's Strategy
A plan or approach devised by an employer to accomplish specific business goals, including hiring, training, and managing employees.
Internal Factor
Elements within an organization that can influence its operations and success, such as culture, employees, or internal processes.
Labour Market Conditions
The dynamics and characteristics of the job market, including the supply and demand for workers, unemployment rates, and wage levels.
Pay Equity
Equal pay for work of equal value.
Q1: A client is receiving 100 mL of
Q3: The nurse is assessing a client in
Q9: What is the general period of protection
Q12: In Zurcher v.Stanford Daily,the Supreme Court held
Q16: In which of the following civil cases
Q63: Fontaine and Monroe are forming a partnership.
Q81: On March 15, Alan Company purchased 10,000
Q118: All of the following are true for
Q182: Long-term investments cannot include:<br>A)Held-to-maturity debt securities.<br>B)Securities with
Q262: Resources such as cash removed from the