Figure 17-8. The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS) curve and two aggregate-demand (AD) curves. On the right-hand diagram, "Inf Rate" means "Inflation Rate."

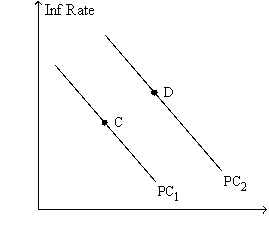
-Refer to Figure 17-8. A movement of the economy from point A to point B, and at the same time a movement from point C to point D, would be described as
Definitions:
Experimental Evidence
Data or information obtained through controlled trials or experiments to test a hypothesis or theory.
Condorcet Paradox
A voting paradox in which collective preferences can be cyclic (non-transitive), meaning no clear winner can be determined through majority rule in a pairwise election.
Voting System
A method or set of rules designed to fairly determine the outcome of elections or decisions based on the collective preferences of participants.
Median Voter Theorem
A principle suggesting that the outcome of a majority vote is most likely to represent the preferences of the voter who is in the middle of the political spectrum.
Q24: Changes in the interest rate<br>A) shift aggregate
Q52: If the stock market crashes, then<br>A) aggregate
Q76: In the early 1970s, the short-run Phillips
Q82: Part of the lag in monetary policy
Q92: If inflation falls,<br>A) people choose to put
Q94: The opportunity cost of holding money<br>A) decreases
Q129: Assuming a multiplier effect, but no crowding-out
Q248: The theory of liquidity preference illustrates the
Q276: In the short run, an increase in
Q292: Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps argued in