Consider the following to answer the question(s) below:
Management styles differ among organizations and may potentially affect employee job satisfaction. A sample of employees was randomly selected from each of three companies with different management styles (Authoritarian, Laissez faire and Participative) and asked to rate their level of job satisfaction on a 10-point scale (10 being the highest level of satisfaction) . The data collected and partial ANOVA results appear below.
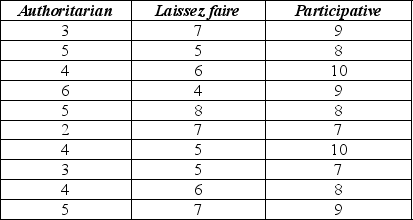

-The P-value for this statistic turns out to be < 0.001. Therefore, at α = 0.05
Definitions:
Marginal Utility
The extra pleasure or benefit gained by a consumer from consuming an additional unit of a product or service.
Utility Function
A mathematical representation of how consumers rank different bundles or combinations of goods according to their level of satisfaction.
Partial Derivative
The derivative of a function of multiple variables with respect to one variable, holding the others constant.
Network Externality
A situation where the value of a product or service increases for a user when more people use it.
Q8: The MSE for the forecasting method used
Q12: The regression coefficients in the seasonal regression
Q18: Which of the following best describes the
Q21: McCain Foods (Canada) of New Brunswick produces
Q27: Consumer Reports Health routinely compares drugs in
Q31: What percent of the variability in cash
Q41: We have calculated a 95% confidence interval
Q138: The return on common stockholders' equity for
Q152: If a company has a high current
Q174: Montgomery Corporation's most recent income statement appears