Table 3-23
Assume that the farmer and the rancher can switch between producing pork and producing tomatoes at a constant rate.
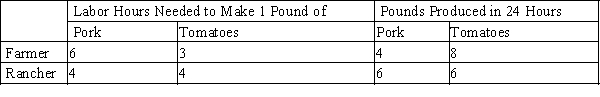
-Refer to Table 3-23. Assume that the farmer and the rancher each has 24 labor hours available. If each person spends all his time producing the good in which he has a comparative advantage and trade takes place at a price of 1 pound of pork for 2 pounds of tomatoes, then
Definitions:
Fixed Cost
Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales, such as rent, salaries, and insurance premiums.
Curvilinear Fashion
Refers to a curve-shaped pattern of growth, progress, or movement in graphs or data analysis.
Variable Costs
Expenses that fluctuate in direct proportion to the amount of production or the volume of sales, including direct labor costs and raw materials.
High-Low Method
A technique in managerial accounting to estimate fixed and variable costs based on the highest and lowest levels of activity.
Q6: Refer to Table 3-23. The opportunity cost
Q74: "If all economists were laid end to
Q143: Trade allows a country to consume outside
Q257: There is only one explanation for why
Q368: Refer to Figure 3-19. Chile has a
Q443: When a relevant variable that is not
Q458: Suppose that when income rises, the demand
Q458: Refer to Figure 3-3. If Dina must
Q463: Refer to Figure 3-3. If Arturo and
Q499: Interdependence among individuals and interdependence among nations