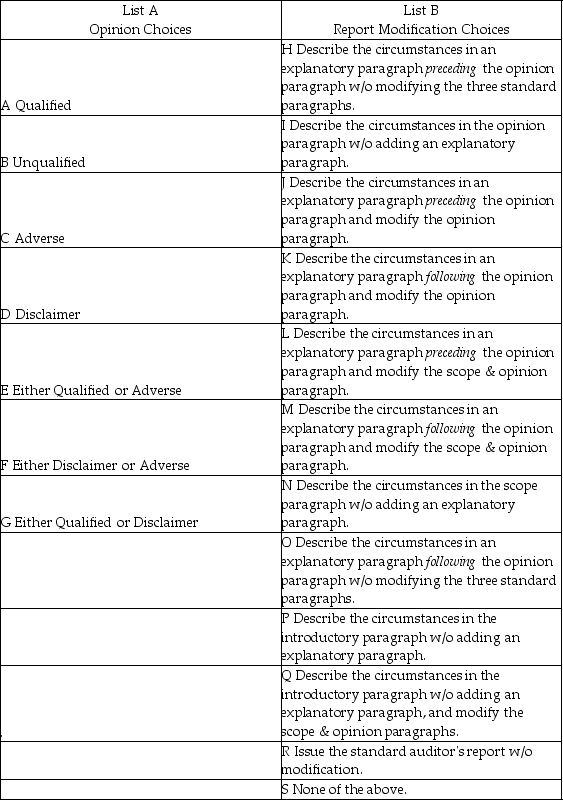
Audit situations 1 through 10 present various independent factual situations an auditor might encounter in conducting an audit. List A represents the types of opinions the auditor ordinarily would issue, and List B represents the report modifications (if any) that would be necessary. For each situation, select one response from List A and one from List B. Select, as the best answer for each item, the action the auditor normally would take. Items from either list may be selected once, more than once, or not at all.
Assume the following:
• The auditor is independent
• The auditor previously expressed an unqualified opinion on the prior-year financial statements unless otherwise noted
• Only single-year (not comparative) statements are presented for the current year (unless otherwise stated)
• The conditions for an unqualified opinion exist unless contradicted in the factual scenario
• The conditions stated in the factual scenario are material
• No report modifications are to be made except in response to the factual scenario
Factual Scenario
1. The financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position, results of operations, and cash flows in conformity with GAAP.
2. In auditing the Long-Term Investments account, an auditor is unable to obtain audited F/S for an investee located in a foreign country. The auditor concludes that sufficient competent evidential matter regarding this investment cannot be obtained but it is not pervasive to the financials as a whole.
3. Due to recurring operating losses and working capital deficiencies the auditor has substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time. However, the F/S disclosures are adequate.
4. The principal auditor decides to refer to the work of another auditor, who audited a wholly owned subsidiary of the entity and issued an unqualified opinion.
5. An entity issues F/S that present financial position and results of operations but omits the related statement of cash flows. Management discloses in the notes to the F/S that it does not believe the statement of cash flows to be useful.
6. An entity changes its depreciation method for production equipment from SL to units of production based on hours of utilization. The auditor concurs with the change, although it has a material effect on the comparability of the entity's F/S.
7. An entity is a defendant in a lawsuit alleging infringement of certain patent rights. However, management. cannot reasonably estimate the ultimate outcome of the litigation. The auditor believes that there is a reasonable possibility of a significant material loss, but the lawsuit is adequately disclosed in the notes to the F/S.
8. An entity discloses certain lease obligations in the notes to the F/S. The auditor believes that the failure to capitalize these leases is a departure from GAAP.
9. The entity wishes to show comparative F/S and include the prior year. However, the prior year F/S contained a qualification due to an inappropriate method of GAAP. Accordingly, management. corrected the prior year GAAP deficiency and included the updated numbers in the comparative financials for the current year.
10. The entity wishes to show comparative F/S and include the prior year. However, the prior year F/S were audited by another auditor who refuses to reissue his opinion.
Definitions:
Problem-Solving Approach
A systematic process of addressing issues or challenges by identifying the problem, analyzing its causes, generating solutions, and implementing them.
Ombudsperson
A neutral intermediary appointed to investigate complaints and mediate fair settlements between parties, especially in an institutional or organizational setting.
Peer-Review Boards
Committees made up of employees who review decisions or actions (such as disputes or grievances) within an organization, offering a form of internal oversight.
Fast-Track
A process or program designed to speed up employee development or career advancement, often by providing intensive training and opportunities.
Q19: If an auditor conducted an audit in
Q28: When auditing the year-end cash balance, one
Q43: If the auditor were responsible for making
Q81: Of the four parts of the AICPA's
Q95: Which of the following is not likely
Q99: Which of the following, if present, would
Q100: Match seven of the terms (a-p) with
Q106: When comparing the auditor's responsibility for detecting
Q109: A CPA firm normally uses one or
Q110: The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 makes destruction