The temperature at the point 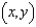 on a metal plate is modeled by
on a metal plate is modeled by 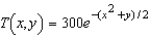 ,
, 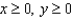 . Find the directions of no change in heat on the plate from the point
. Find the directions of no change in heat on the plate from the point 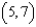 .
.
Definitions:
Memory Consolidation
The process by which short-term memories are transformed into long-term memories.
Long-Term Potentiation
An enduring increase in signal transmission between two neurons that results from stimulating them synchronously, believed to be a cellular mechanism for learning and memory.
Classically Conditioned Associations
Refers to the learning process that occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired together; a response that is at first elicited by the second stimulus is eventually elicited by the first stimulus alone.
Cerebellum
is a part of the brain that plays a major role in motor control, balance, coordination, and fine-tuning of movements.
Q1: Determine the continuity of the function <img
Q5: Evaluate the iterated integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4584/.jpg" alt="Evaluate
Q6: Suppose a pharmaceutical corporation has two plants
Q11: Sketch the level curves of the function
Q11: Set up an integral for both orders
Q14: Evaluate the line integral using the Fundamental
Q14: Sketch the curve represented by the parametric
Q16: Find the area of the portion of
Q18: Find the volume of the parallelepiped with
Q19: Find the rectangular equation for the surface