The smaller the curvature in a bend of a road, the faster a car can travel. Assume that the maximum speed around a turn is inversely proportional to the square root of the curvature. A car moving on the path 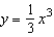 (x and y are measured in miles) can safely go 25 miles per hour at
(x and y are measured in miles) can safely go 25 miles per hour at 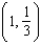 . How fast can it go at
. How fast can it go at 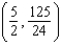 ? Round your answer to two decimal places.
? Round your answer to two decimal places.
Definitions:
Zero Economic Profits
Zero economic profits occur in a competitive equilibrium when firms earn just enough revenue to cover their total costs, including the opportunity costs.
Short Run
A period of time during which at least one of a firm's inputs is fixed, limiting its ability to increase production.
Long Run
A period in economics in which all factors of production and costs are variable, allowing for full adjustment to changes.
Total Revenue
Total revenue is the total income generated by a company from its sales of goods or services before any expenses are subtracted.
Q3: Consider the series <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4584/.jpg" alt="Consider the
Q5: Find the eccentricity of the polar equation
Q5: The radius of a right circular cylinder
Q8: Explain how to use the geometric series
Q8: Use the polynomial test to determine whether
Q11: Find the directional derivative of the function
Q14: Find an equation of the hyperbola with
Q15: Evaluate the following iterated integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4584/.jpg"
Q17: Find an equation of a plane passing
Q19: The terms of a series <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4584/.jpg"