Hooke's Law states that the force F required to compress or stretch a spring (within its elastic limits) is proportional to the distance d that the spring is compressed or stretched from its original length. That is, 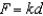 where k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring and is called the spring constant. The table shows the elongation d in centimeters of a spring when a force of F newtons is applied. Use a graphing utility to plot the data and graph the linear model.
where k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring and is called the spring constant. The table shows the elongation d in centimeters of a spring when a force of F newtons is applied. Use a graphing utility to plot the data and graph the linear model. 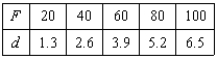
Definitions:
Annual Interest
The total amount of interest due over the course of a year on a loan or financial product.
Interest Expense
The cost incurred by an entity for borrowed funds over a period of time, typically reported on the income statement.
Semiannual Interest
Interest calculated and paid on a loan or bond two times a year.
Straight-line Method
A method of calculating depreciation of an asset by evenly spreading its cost over its useful life.
Q1: What is generally the preferred medium of
Q1: Find the derivative of the function. <img
Q1: What is meant by the biopsychosocial model?
Q5: Match the function <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4584/.jpg" alt="Match the
Q7: Use Newton's Method to approximate the zero(s)
Q10: An eating disorder in which a person
Q11: What issues might a gay man face
Q12: Find an equation of the line that
Q19: Why are images of humans traditionally banned
Q20: What is the content of Jean-Michel Basiquiat's