A moving object has a position vector function 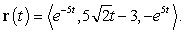
A) Find the speed of the object at time 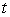 .
.
B) Find the distance traveled by the object between times 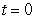 and
and 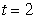 .
.
C) When does the object have minimum speed?
Definitions:
Neurons
The basic working unit of the brain, a specialized cell designed to transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells.
Isotonic Saline
A solution of sodium chloride (salt) in water at a concentration that matches the salt concentration of the body cells and blood, commonly used for medical hydration and wound cleaning.
Extracellular Fluid
The body fluid outside cells, providing a medium for substances to pass between cells and blood vessels.
Resting Membrane Potential
The electrical charge difference across the cellular membrane when a neuron or muscle cell is at rest, typically around -70 mV.
Q9: The angle between two intersecting lines is
Q17: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Let .
Q22: Find the surface area of the surface
Q27: Compute the line integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Compute
Q28: The curves orthogonal to the solutions of
Q46: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Let be
Q50: Give the polar coordinates of the point
Q63: Determine whether the series <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Determine
Q69: Write the equation of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Write
Q89: The position of a particle for time