On a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, 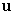 is the position vector from the origin to the point
is the position vector from the origin to the point 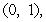 and
and 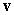 is the position vector with length
is the position vector with length 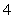 at an angle
at an angle 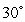 to the positive x-axis. Find the vectors.
to the positive x-axis. Find the vectors.
A) 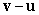
B) 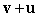
Definitions:
Proximity
The proximity or emotional connection among individuals, things, or concepts, frequently affecting their relations and engagements.
Mere Exposure Effect
The tendency of people to like things more just because they recognize them.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
A belief or expectation that an individual holds about a future event that manifests because the individual holds it.
Self-Disclosure
The act of revealing personal, private information about oneself to others, facilitating intimacy and trust in relationships.
Q7: A particle travels along a path <img
Q11: Which of the following equations describes the
Q29: A deer population for a certain area
Q33: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Let .
Q41: Calculate the Maclaurin polynomial <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Calculate
Q46: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Let be
Q66: For the plane <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="For the
Q73: Evaluate the integral <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q77: Find the centroid of the region enclosed
Q89: A radioactive radiation with strength <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg"