The following function is a counterexample for the converse of the Intermediate Value Theorem, which states:
If 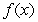 assumes all the values between
assumes all the values between 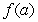 and
and 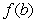 in the interval
in the interval 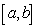 , then
, then 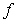 is continuous on
is continuous on 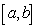 :
:
Definitions:
Status Position
The rank or standing of an individual or group within a societal or organizational hierarchy.
Group Cohesion
A property of a group, specifically the degree to which members of a group desire to remain in that group and resist leaving it. A highly cohesive group will maintain a firm hold over its members’ time, energy, loyalty, and commitment.
Task Cohesion
Task cohesion refers to the level of unity and commitment among members of a group or team towards achieving a common goal.
Social Cohesion
The bonds or "glue" that bring people together in society, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support.
Q7: Suppose the Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used
Q9: Find the minimum and maximum values of
Q14: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Let be
Q16: If the landowner is risk averse he
Q39: True or False: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="True
Q41: Find <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Find and
Q41: The derivative of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="The derivative
Q45: Calculate the volume of the solid obtained
Q57: Consider the following functions. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q62: Use the global extrema of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg"