The following function is a counterexample for the converse of the Intermediate Value Theorem:
If 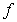 assumes all the values between
assumes all the values between 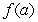 and
and 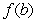 in the interval
in the interval 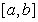 then
then 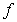 is continuous on
is continuous on 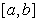 :
:
Definitions:
2-for-1 Split
A stock split in which a company divides its existing stock into two shares, effectively halving the price of each share while doubling the number of shares owned by shareholders.
5-for-3 Split
A type of stock split where shareholders receive 5 shares for every 3 shares they hold, effectively increasing the share quantity and adjusting the stock price downward.
Shares
Units of ownership interest in a corporation or financial asset that provide for an equal distribution in any profits, if any are declared, in the form of dividends.
Franchise
A type of license that grants a franchisee access to a franchisor's proprietary knowledge, processes, and trademarks, to allow the party to sell a product or provide a service under the business's name.
Q2: A company that manufactures health food snacks
Q2: How much money will an investment of
Q3: Let V be the volume of a
Q7: Find a value <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Find a
Q28: The dominant component in this time series
Q49: We have created a 95% confidence interval
Q50: The volume of a sphere of radius
Q63: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5596/.jpg" alt="Let ,
Q64: A 3-kg object is dropped from a
Q72: Find the volume of the solid obtained