When a spring is stretched and then released, it oscillates according to two laws of physics: Hooke's Law and Netwon's Second Law. These two laws combine to form the following differential equation in the case of free, undamped oscillation: 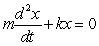 where m is the mass of an object attached to the spring, x is the distance the spring is stretched beyond its standard length with the object attached (its equilibrium point) , t is time, and k is a constant associated with the strength of the spring. Consider a spring with
where m is the mass of an object attached to the spring, x is the distance the spring is stretched beyond its standard length with the object attached (its equilibrium point) , t is time, and k is a constant associated with the strength of the spring. Consider a spring with 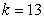 from which is hung a 40-pound weight. The spring with the weight attached stretches to its equilibrium point. The spring is then pulled 7 feet farther than its equilibrium and released. Find a particular solution for the position of the spring after time t. Use the fact that
from which is hung a 40-pound weight. The spring with the weight attached stretches to its equilibrium point. The spring is then pulled 7 feet farther than its equilibrium and released. Find a particular solution for the position of the spring after time t. Use the fact that 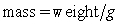 , where g is the gravitational constant 32 feet per second per second, and that when the spring is first released, its velocity is zero. Round the coefficients to three decimal places.
, where g is the gravitational constant 32 feet per second per second, and that when the spring is first released, its velocity is zero. Round the coefficients to three decimal places.
Definitions:
Reasonably Competent Accountant
A professional who possesses the necessary skills and knowledge expected of a qualified accountant in performing their duties.
Circumstances
The specific conditions or facts affecting a situation, event, or action which can influence the outcome.
Accountant-client Privilege
A legal privilege that allows clients to refuse to disclose confidential communications with their accountants in legal proceedings.
Statutorily Recognized
Officially acknowledged or established by law through legislative action.
Q8: Sid rents an apartment from Town Properties,
Q10: The number of patents issued for a
Q11: Scientists can model the change in snow
Q17: According to Immanuel Kant, we should be
Q17: There is a well-established defense to a
Q23: Whenever we use the word "good," we
Q29: Property Management Corporation (PMC) owns several apartment
Q31: Civil law systems are typically seen in
Q46: Charging different prices to different buyers for
Q62: Haya obtains an insurance policy from Inviolable