When a spring is stretched and then released, it oscillates according to two laws of physics: Hooke's Law and Netwon's Second Law. These two laws combine to form the following differential equation in the case of free, undamped oscillation: 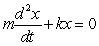 where m is the mass of an object attached to the spring, x is the distance the spring is stretched beyond its standard length with the object attached (its equilibrium point) , t is time, and k is a constant associated with the strength of the spring. Consider a spring with
where m is the mass of an object attached to the spring, x is the distance the spring is stretched beyond its standard length with the object attached (its equilibrium point) , t is time, and k is a constant associated with the strength of the spring. Consider a spring with 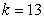 from which is hung a 40-pound weight. The spring with the weight attached stretches to its equilibrium point. The spring is then pulled 7 feet farther than its equilibrium and released. Find a particular solution for the position of the spring after time t. Use the fact that
from which is hung a 40-pound weight. The spring with the weight attached stretches to its equilibrium point. The spring is then pulled 7 feet farther than its equilibrium and released. Find a particular solution for the position of the spring after time t. Use the fact that 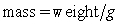 , where g is the gravitational constant 32 feet per second per second, and that when the spring is first released, its velocity is zero. Round the coefficients to three decimal places.
, where g is the gravitational constant 32 feet per second per second, and that when the spring is first released, its velocity is zero. Round the coefficients to three decimal places.
Definitions:
Linguistic
Pertaining to language, including its structure, use, and the study of its properties and function.
Spatial
Relating to, occupying, or having the character of space, often used in context with one's ability to judge size, distance, or the relationship between objects in space.
Interpersonal
Pertaining to the connections or associations between individuals.
Spatially Analyzing
The process of examining locations, attributes, and relationships through space to understand patterns and trends.
Q2: Federal district courts are bound by the
Q4: Because the consideration on option contracts is
Q8: Sid rents an apartment from Town Properties,
Q8: It is presumed that a co-tenancy is
Q12: Draw the contour curves <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6775/.jpg" alt="Draw
Q21: Determine whether the function is continuous or
Q27: A person learns a new task at
Q39: Test for relative maxima and minima. <img
Q40: In Board of Control of Eastern Michigan
Q41: For a region, the percentage of adults