Suppose the rate of change of the percentage of low-birthweight babies (less than 5 pounds 8 ounces) in 2000 can be modeled by 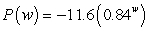 percentage points per pound when the mother gains w pounds during pregnancy. The model is valid for the weights between 18 and 43 pounds. Estimate, to two decimal places, the area of the region between the graph of P and the w-axis from
percentage points per pound when the mother gains w pounds during pregnancy. The model is valid for the weights between 18 and 43 pounds. Estimate, to two decimal places, the area of the region between the graph of P and the w-axis from 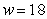 to
to 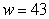 using 5 midpoint rectangles. Interpret your answer.
using 5 midpoint rectangles. Interpret your answer.
Definitions:
Psychoanalytic Theory
A theory of personality organization and the dynamics of personality development that guides psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud.
Social Cognitive Theory
A theory in psychology that suggests learning occurs in a social context and can happen purely through observation or direct instruction, even in the absence of motor reproduction or direct reinforcement.
Coregulation Theory
A concept in psychology that suggests a dynamic, reciprocal relationship in emotional or behavioral regulation between individuals, such as in close relationships.
Cognitive-Developmental Theory
A theory of the stages through which children's cognitive abilities develop, originally proposed by Jean Piaget, highlighting the importance of mental processes in understanding the world.
Q3: Which of the following is a fair
Q10: In Katko v. Briney, the court held
Q12: In SouthTrust Bank v. Williams, which of
Q12: Evaluate the function at the given values
Q27: Calculate the derivative of the function with
Q34: A function and its first and second
Q35: At common law, the modification of an
Q35: Find a general solution for the following
Q40: The willingness of saddle producers to supply
Q64: The government of Japan sets a limit