A table of selected values for a function is given. Also shown are tables of values for the derivative and the accumulation function with 0 as the starting point. Determine which table contains the values of the derivative, 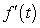 , and which contains the values of the accumulation function,
, and which contains the values of the accumulation function, 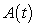 . Justify your choice.
. Justify your choice. 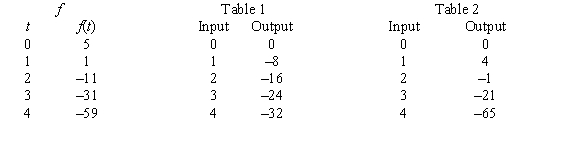
Definitions:
Addiction
A chronic condition characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, despite adverse consequences.
Solomon
Richard L. Solomon was an American psychologist known for his work on the opponent-process theory of emotions, which explains complex emotional and motivational states.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Physical and mental effects experienced when a person stops using or reduces intake of a psychoactive substance to which they have become addicted.
Opponent Process Theory
A psychological and neurological model that explains how the perception of colors is controlled by the operation of opposing neural systems.
Q1: Find <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6775/.jpg" alt="Find
Q1: An unintentional killing that takes place during
Q7: A process to extract pectin and pigment
Q7: The rate of change with respect to
Q8: Sid rents an apartment from Town Properties,
Q23: What are the functions of law?
Q28: a(n. _ is a UCC option made
Q29: According to contract law, promise-breaking without a
Q39: Test for relative maxima and minima. <img
Q44: Fatty acids are liberated from a fat