The volume V (in liters) of a certain mass of gas is related to its pressure P (in millimeters of mercury) and its temperature T (in degrees Kelvin) by the law 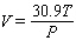 Compute
Compute 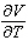 and
and 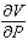 when T = 260 and P = 700.
when T = 260 and P = 700.
Definitions:
Stock Price
The cost of purchasing a share of a company in the stock market at any given time.
Sharpe Measure
A metric used to evaluate the risk-adjusted return of an investment portfolio, comparing its excess return to the standard deviation of the portfolio's returns.
Risk-Free Return
The theoretical return on an investment with zero risk of financial loss, typically associated with government bonds.
Time-Weighted Return
A method to measure the rate of return of an investment portfolio which eliminates the distorting effects of inflows and outflows of money.
Q5: The _property is valuable because it cuts
Q6: What is helpful when subtracting mixed number
Q10: The term algebraic thinking is used instead
Q10: Different models are used to help illustrate
Q11: Each the statements below are examples of
Q14: Which problem represents the separate,start unknown structure?<br>A)Maryann
Q41: Based on a preliminary report by a
Q91: Evaluate the definite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6026/.jpg" alt="Evaluate
Q118: Evaluate the definite integral by using the
Q200: Find the volume of the solid bounded