The volume V (in liters) of a certain mass of gas is related to its pressure P (in millimeters of mercury) and its temperature T (in degrees Kelvin) by the law 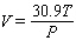 Compute
Compute 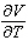 and
and 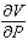 when T = 260 and P = 700.
when T = 260 and P = 700.
Definitions:
Standard Costs
Predetermined or estimated expenses that are often used to measure and control the cost of producing a product or performing a service.
Management Tool
A management tool is any device, technique, or software used to manage an organization's processes, resources, or data effectively.
Fixed Factory Overhead Volume Variance
The difference between the budgeted and actual fixed overhead costs attributed to a variation in produced units volume.
Supervisors
Individuals who have the responsibility to oversee and direct the work of others, ensuring that tasks are completed effectively and efficiently.
Q9: The full process of doing meaningful statistics
Q17: What is a common misconception with fraction
Q50: Use the table of integrals to find
Q87: Evaluate the definite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6026/.jpg" alt="Evaluate
Q145: The average waiting time for patients arriving
Q152: Suppose an investment is expected to generate
Q158: Evaluate the definite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6026/.jpg" alt="Evaluate
Q161: Find the first partial derivatives of the
Q229: Determine whether the given function is a
Q248: Find the area of the region under