Let 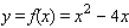 . Find the average rate of change of y with respect to x in the interval from
. Find the average rate of change of y with respect to x in the interval from 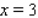 to
to 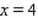 , from
, from 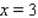 to
to 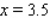 , from
, from 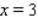 to
to 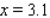 , and the (instantaneous) rate of change of y at
, and the (instantaneous) rate of change of y at 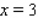 .
.
Definitions:
Classical Conditioning
A habituation procedure where two stimuli are paired frequently, and a reaction that initially occurs because of the second stimulus subsequently occurs due to the first stimulus exclusively.
Cognitive Map
A mental representation of one’s physical environment, facilitating navigation and understanding of spatial relationships.
Observational Learning
Learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others, also known as social learning or modeling.
Classical Conditioning
An educational method where learning happens by linking an external stimulus with a naturally existing stimulus.
Q29: Lupe deposits a sum of $5,000 into
Q37: The number of IBM shares that Nancy
Q40: Perform the indicated operations and simplify the
Q62: Find an equation of the line that
Q112: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6026/.jpg" alt="Let ,
Q152: A furniture store offers free setup and
Q156: If an open box has a square
Q195: The function P, whose graph follows, gives
Q236: The demand equation is <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6026/.jpg" alt="The
Q307: Suppose <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6026/.jpg" alt="Suppose measures