Two independent samples of sizes 20 and 30 are randomly selected from two normally distributed populations. Assume that the population variances are unknown but equal. In order to test the difference between the population means, 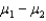 , the sampling distribution of the sample mean difference,
, the sampling distribution of the sample mean difference, 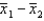 , is:
, is:
Definitions:
P-Value
The likelihood of encountering test outcomes as significant as or more than the actual observed results, assuming the null hypothesis is valid.
Null Hypothesis
The proposition that observed differences among specific populations are attributed to errors in sampling or experimentation, hence indicating no major divergence.
Level Of Significance
The threshold chosen for deciding whether an observed effect is statistically significant, usually denoted by alpha.
Hypotheses
Plural form of hypothesis, which are propositions or statements made for the sake of argument that are tested through research and experimentation.
Q1: Which of the following statements concerning materiality
Q6: What effect does the auditee's use of
Q14: CAS 240 requires auditors to ignore the
Q22: In a multiple regression model, the following
Q24: After obtaining an understanding of the internal
Q45: An economic motive for fraud is the
Q47: The audit objective specifying that "all recorded
Q73: The F-test used for testing the difference
Q145: When testing <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4382/.jpg" alt="When testing
Q162: Which of the following conditions is needed