Arsenic acid is a triprotic acid in water,ionizing in the following sequential steps:
H3AsO4 + H2O H2AsO4- + H3O+
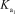 = 5.5 *10 - 3
= 5.5 *10 - 3
H2AsO4- + H2O HAsO42- + H3O+
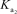 = 1.7 *10-7
= 1.7 *10-7
HAsO42- + H2O AsO43- + H3O+
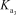 = 5.1 * 10-12
= 5.1 * 10-12
What is the approximate pH of a 0.80 M Na3AsO4 solution?
Definitions:
Interest
The cost of borrowing money or the payment received for saving or investing money, typically expressed as an annual percentage of the principal.
Nominal Rate
The interest rate stated on a financial product, not adjusted for inflation.
Effective Rate
The actual interest rate an investor earns or pays on an investment or loan, taking into account the effects of compounding.
Compounding Interval
The frequency at which interest is added to the principal amount of an investment or loan, influencing the total amount of interest earned or paid.
Q11: For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>,the
Q50: Electrochemical cell potentials can be used
Q52: A concentration cell with a cell
Q54: Explain why Ni(CN)<sub>4</sub><sup>2</sup><sup>-</sup> is diamagnetic and NiCl<sub>4</sub><sup>2</sup><sup>-</sup>
Q61: Which d orbital(s)is/are highest in energy in
Q69: Determine the activation energy,E<sub>a</sub>,of the decomposition
Q84: Hydrofluoric acid,HF,dissociates in water according to
Q112: Choose the complex that you predict will
Q130: Determine <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\Delta"><span class="katex"><span
Q139: For the chemical equilibrium aA +