Given the following data,determine the rate constant,k,of the reaction: H2(g) + 2 ICl(g) I2(g) + 2 HCl(g) 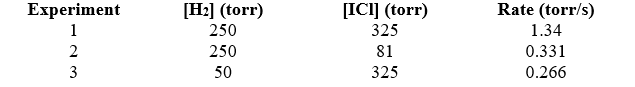
Definitions:
Depth-of-processing Approach
A theory that suggests the depth at which information is thought about or processed affects how well it is remembered; deeper processing involves meaningful analysis and leads to better recall.
Interference Theory
The theory suggesting that the ability to remember information is affected by other learning, leading to memory interference and forgetting.
Stage Theory
A theory that development occurs in distinct phases or stages, each characterized by specific criteria.
Retrograde Amnesia
A condition involving the loss of memory for events that occurred before the onset of the amnesia.
Q43: Ethylene glycol is used in automobile
Q51: If one mole of each of the
Q95: Given the following data,determine the order
Q115: Given the following data,determine the order
Q117: What is the entropy change in
Q124: Which one of the ionic compounds below
Q134: Identify the equilibrium expression for the
Q143: Intravenously administered saline solution must have
Q190: Sometimes liquid ammonia,NH<sub>3</sub>,is used as a solvent
Q226: K<sub>sp</sub> for mercury(II)iodide is 2.8