Consider the representations below to answer the next three questions.
(I) 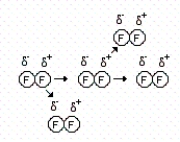 (II)
(II) 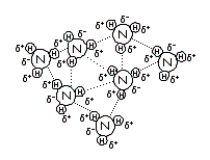 (III)
(III) 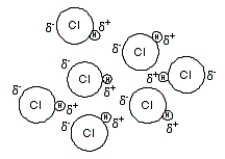
-How many of the following statements are correct concerning drawing I?
I.Each molecule induces a dipole onto the next molecule in close proximity.
II.The phenomenon shown is relatively weak and short-lived.
III.C8H18 contains this type of interaction.
IV.The forces that exist in this example are London dispersion forces.
Definitions:
Marginal Productivities
The additional output derived from the addition of one more unit of a factor of production, keeping all other inputs constant.
Electronic Pulse
A burst of electromagnetic energy produced by a sudden electrical charge, often associated with electromagnetic weapons or natural phenomena like lightning.
Marginal Product
The additional output that is produced by employing one more unit of a specific factor of production, holding all other factors constant.
Population Decrease
A reduction in the number of people in a specific area, often due to factors like decreasing birth rates or emigration.
Q4: Steel is considered to be a(n)_.<br>A)interstitial alloy<br>B)ionic
Q7: The following data were obtained for
Q28: Let f(x, y) = <span
Q67: Express the number <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6423/.jpg" alt="Express the
Q77: If vectors a, b, and c
Q78: The reaction 3NO <span class="ql-formula"
Q81: Which of the following statements best describes
Q106: The sodium salt,NaA,of a weak acid is
Q137: Find the Taylor polynomial <span
Q250: Describe the surface whose equation in