Let where f is the function whose graph is shown below: 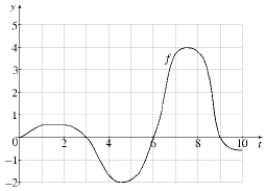 (a) Use the Comparison Properties of Integrals to estimate the value of the following integrals:
(a) Use the Comparison Properties of Integrals to estimate the value of the following integrals:
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (b) At what values of x does g have a local maximum or minimum?
(c) At what values of x does g attain its absolute maximum or minimum?
Definitions:
Octants
One of eight equal parts into which a three-dimensional space can be divided by three mutually perpendicular planes.
Fiedler's Contingency Theory
A leadership model asserting that the effectiveness of a leader's style is contingent on the situational context, including the leader's relationships with followers and task structure.
LPC
Least Preferred Coworker scale, a tool used in Fiedler's Contingency Theory to measure a leader's task or relationship orientation.
Leadership
The act or ability of leading a group towards achieving a common goal, often involving inspiring and guiding others.
Q26: Which of the following is a
Q54: Assume the half-life of carbon 14 is
Q63: A tank contains water. The end of
Q79: A gas pipeline is to be constructed
Q89: A 100-foot length of steel chain weighing
Q124: Find the volume of the solid
Q125: Let <span class="ql-formula" data-value="f (
Q131: Which of the following is a
Q144: Determine whether each integral is convergent
Q172: Find each of the following limits