Wild-type mice are adoptively transferred with naive CD4 T cells isolated from OT-II T-cell receptor transgenic mice. These OT-II T cells are specific for a peptide of the chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) bound to MHC class II. After transfer, the OT-II cells rapidly disperse to all of the secondary lymphoid organs in the recipient mice. Half of the recipient mice are then given OVA protein dissolved in their drinking water, and the other half of the mice receive normal drinking water for 5 days. On the following day (day 6), lymphocytes from the spleen, the peripheral lymph nodes (LN), mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), Peyer's patches (PP) and lamina propria (LP) are isolated and examined for the proportions of CD4 T cells in each organ expressing FoxP3. The results are shown in Figure. 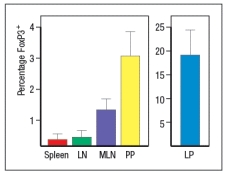
a) What is the conclusion from this experiment?
To investigate this further, dendritic cells are isolated from the spleen (spl-DC) or from the lamina propria of the small intestine (LP-DC). Each subset of dendritic cells is pulsed with the OVA protein, and then incubated with naive OT-II CD4 T cells for 5 days in the presence or absence of TGF- . The CD4 T cells are then examined for FoxP3 expression; the results are shown in Figure. 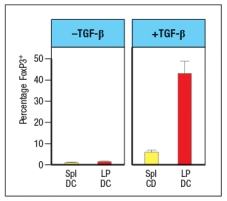
b) Why is TGF- added in this experiment?
c) What is the major difference between the splenic dendritic cells and those isolated from the lamina propria?
The CD4 T cells from the experiment above, in which the T cells were cultured for 5 days with OVA-pulsed splenic or lamina propria dendritic cells in the presence or absence of TGF- , were also assessed for their surface expression of the integrin 4 7.
d) Of the four groups of T cells shown in the graph, which ones would be expected to show high levels of 4 7?
Definitions:
Underapplied Overhead
The situation where the allocated overhead costs are less than the actual overhead incurred.
Proration
The method of allocating proportions of expenses or incomes across different departments, products, or periods.
Process Costing
An accounting methodology used for homogenous products, which assigns costs to each production unit based on processes or departments.
Petroleum Refining
The industrial process of transforming crude oil into useful products such as fuel, lubricants, and petrochemicals.
Q1: An area of cancer immunotherapy that is
Q6: Eosinophils are a subset of granulocytes
Q9: In a mixed lymphocyte reaction, T cells
Q10: MHC class I surface expression is dependent
Q12: Composed of antigens purified from microbes or
Q14: Synthesis question: For the last five years,
Q14: P-selectin<br>A)B7-1,B7-2<br>B)Class II MHC<br>C)LFA-3<br>D)VCAM-1<br>E)Sialylated Lewis X
Q19: The mechanism of cross-presentation by dendritic cells
Q23: Conjugate vaccines, such as those developed against
Q80: i. A forecast is considered necessary in