Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacterium that colonizes the mucosal surface of the upper respiratory tract in humans. The presence of this bacterium in the nose and throat is widespread in the population, and in most people, colonization with Strep. pneumoniae is asymptomatic. Figure shows a comparison of in vitro growth curves of the wild-type strain of Strep. pneumoniae, as well as a Strep. pneumoniae mutant strain with a defect in one bacterial gene. The graph on the right shows the growth curve following addition of lysozyme during the logarithmic phase of bacterial growth. 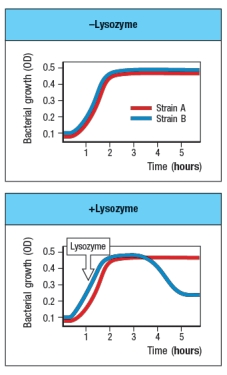
Which statement could account for the data in these graphs?
Definitions:
Prereflective Thinking
A level of cognition occurring without conscious awareness or reflection on the thought process itself.
Dialectical Reasoning
A method of argument that involves the contradiction between two interacting forces, leading to their resolution and the development of a synthesis.
Contextual Intelligence
The ability to understand the limits of our knowledge and to adapt that knowledge to an environment different from the one in which it was developed.
Formal Reasoning
The process of following a set of rigorous procedures or rules to arrive at a conclusion, often used in mathematics and logic.
Q7: Each immunoglobulin (Ig) domain is composed
Q13: Determine the expected opportunity loss for the
Q15: Early studies analyzing the antibody protein fragments
Q21: In some cases, antibody binding to a
Q32: Diacyl-glycerol (DAG) is one of the
Q36: i. An index of 239.2 and an
Q52: A survey of the opinions of property
Q65: An index of clothing prices for 2014
Q72: The Consumer Price Index (1982-84 = 100)
Q80: The average weekly earnings (including overtime) in