Four different clinical isolates of the Gram-positive bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus, are tested for their abilities to resist innate immune defense mechanisms. For these experiments, each bacterial strain is first grown in culture to achieve log-phase replication, and then cultures are supplemented with dilutions of human serum containing normal serum proteins as well as antibodies capable of binding to S. aureus. One hour later, the cultures are analyzed and the numbers of live bacteria are quantitated. The data from this experiment are shown in Figure .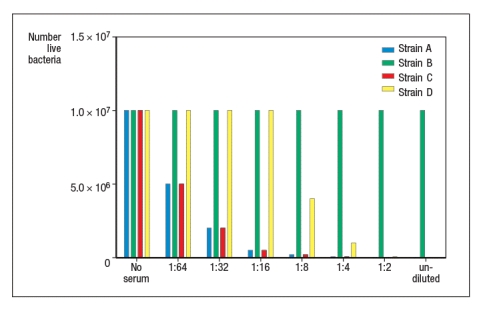
a) From these data, what general conclusions can be reached about the four strains of S. aureus?
To identify the bactericidal mechanisms killing each strain of S. aureus, the serum is depleted of complement C3 by running it over an anti-complement C3 antibody affinity column. The experiment above is then repeated and the data are shown in Figure .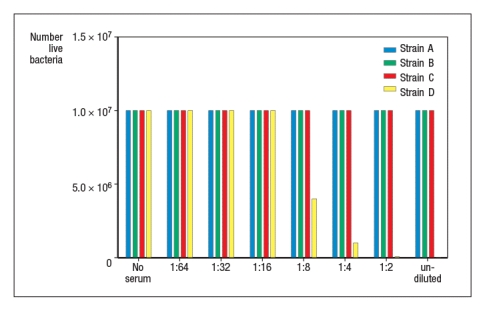
b) What is the most likely mechanism accounting for the killing of strain D in this experiment?
To determine whether strains A and C are susceptible to the same microbicidal pathway, the serum is depleted of antibody by running over an anti-human immunoglobulin affinity column. Following this treatment, it is found that strain A, but not strain C is still killed by incubation with the serum.
c) From these data, what is the most likely mechanism killing S. aureus strain A? What about strain C?
Definitions:
Ethical
Related to moral principles or the branch of knowledge dealing with these.
Liquidated Debt
A debt where the amount owed is known and determined, not subject to future conditions.
Unliquidated Debt
A debt that has not been determined or calculated because the exact amount owed may not be known.
Consideration
The value (monetary, goods, services, promise) that is given by both parties in a contract, making the agreement legally binding.
Q1: Celiac disease occurs when an individual
Q10: The states of nature are:<br>A) the choices
Q11: i. Social security, old-age pensions, many apartment
Q22: Cytotoxic effector T cells also produce
Q26: A decision tree:<br>A) uses a box to
Q31: NK cells can be activated following recognition
Q36: Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is an immunodeficiency disease due
Q40: i. The irregular component of a time
Q84: To analyze data cross-classified in a
Q110: A student asked a statistics professor