The immune system uses several types of effector modules to protect us against different categories of pathogens. Four major types of pathogens are shown in Figure . 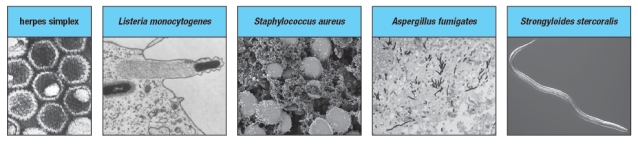
a) Which of these categories might be effectively eliminated by innate immune responses that include antimicrobial peptides and phagocytic cells such as neutrophils and macrophages? Explain your answer.
b) Which of these categories of pathogenic organisms might be most effectively dealt with by antibodies, if the innate response is insufficient for their eradication?
c) Which of these categories of pathogenic organisms would require T lymphocyte responses for their elimination?
Definitions:
Indirect Approach
A method often used in preparing cash flow statements where net income is adjusted for non-cash transactions and changes in working capital.
Investing Activities
Transactions involving the purchase and sale of long-term assets and investment securities, as part of a company’s cash flow activities.
Financing Activities
Transactions involving raising capital and repaying investors, including issuing equity or debt, and dividend payments.
Common Stock
Equity ownership in a corporation, with voting rights and potential dividends, not having preference over preferred stock in bankruptcy proceedings.
Q11: How will data which increases (or decreases)by
Q11: Recently, students in a marketing research class
Q11: For each of the panels A–D in
Q16: A distributor of personal computers has five
Q25: Listed below is the net sales in
Q50: If the coefficient of multiple determinations is
Q57: i. An index is a convenient way
Q72: The personnel manager is concerned about absenteeism.
Q88: i. In a time series analysis, the
Q114: A survey of the opinions of property