Water movement is important in urine formation in the kidneys. Urine is formed when the blood is filtered by the kidneys into kidney tubules. Three figures are presented here that relate to how the kidney tubules respond to the administration of the hormone vasopressin. The direction that water flows in these figures is from the kidney tubules back into the blood.
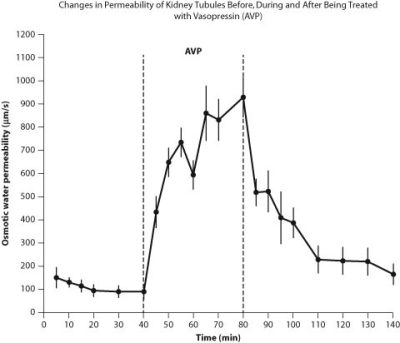 Figure A. Changes in permeability of tubules in the kidney in response to the hormone vasopressin (AVP) , which aids in osmoregulation.
Figure A. Changes in permeability of tubules in the kidney in response to the hormone vasopressin (AVP) , which aids in osmoregulation.
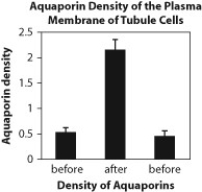 Figure B. Density of aquaporins in kidney tubule cells before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
Figure B. Density of aquaporins in kidney tubule cells before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
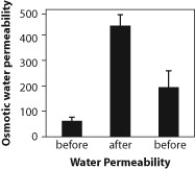 Figure C. Permeability of tissues to water before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
Figure C. Permeability of tissues to water before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
-Based on the data from these figures, what do you expect the urine of a person to be like when vasopressin is having an effect on the kidney tubules?
Definitions:
Organic Product
Organic product often refers to a molecule resulting from organic synthesis, especially in the context of organic reactions.
Methanol
The simplest alcohol, with the chemical formula CH3OH, used as a solvent, antifreeze, fuel, and in the production of formaldehyde.
Ethanol
A two-carbon alcohol (C2H5OH) commonly used as a solvent, fuel, and in alcoholic beverages.
Methylhexene
An alkene with a methyl group and a hexene (six carbon linear chain with a double bond) component in its structure.
Q7: About how much of the energy in
Q10: Species in widely separated but similar biomes
Q11: Which of the following statements regarding the
Q15: Which of the following statements regarding membrane
Q18: What is one main effect of auxins
Q19: Based on the age structure of the
Q27: Small areas that are home to a
Q43: An object covers a distance of 8
Q51: If an object moves with constant acceleration,its
Q70: Sickle-cell disease is an example of<br>A) pleiotropy.<br>B)