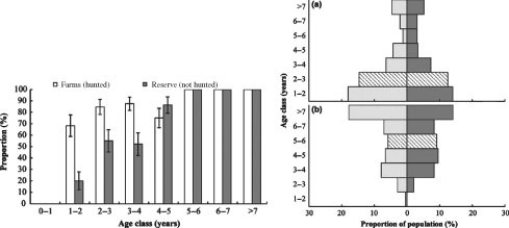
In southern Africa, jackals are major predators of livestock on farms. As a control measure, farmers often kill jackals they find on their farms. Scientists Liaan Minnie and colleagues predicted that increased mortality of jackals would result in altered life history traits of this carnivore species. To test their predictions, they compared the number of pregnant female jackals in different age classes in populations that were hunted (on farms) to those that were not hunted (in conservation reserves) . The resulting pattern shown in the first graph is the proportion of females that are pregnant in each age class. The scientists also collected demographic data to construct age structure diagrams (second graph) of jackals in (a) hunted populations (farms) and (b) populations that were not hunted (reserves) . In the age structure diagram, males are plotted on the left, females are plotted on the right, and the median age class is denoted with hatched bars.
 Source: Minnie, L., Gaylard, A., & Kerley, G. I. (2016) . Compensatory life‐history responses of a mesopredator may undermine carnivore management efforts. Journal of Applied Ecology, 53(2) , 379-387.
Source: Minnie, L., Gaylard, A., & Kerley, G. I. (2016) . Compensatory life‐history responses of a mesopredator may undermine carnivore management efforts. Journal of Applied Ecology, 53(2) , 379-387.
-Jackals live in socially organized groups, with dominant females suppressing reproduction in nondominant (submissive) individuals. Examine the first graph, and select the explanation that best predicts the effect of dominance hierarchies on population growth in jackals.
Definitions:
Fetal Skull
The bony structure forming the head of the fetus, characterized by soft spots called fontanelles that allow for compression during birth.
Intramembranous Bones
Bones that develop directly within sheets of connective tissue, such as the skull's flat bones.
Hyaline Cartilage
A translucent type of cartilage found on many joint surfaces, characterized by its glassy appearance.
Fetal Skull
The fetal skull is the soft, flexible head structure of a fetus that is designed to aid in the birth process by slightly deforming as it passes through the birth canal.
Q12: The prokaryotes that cause tooth decay have
Q30: You are told that the song of
Q32: Which structure constitutes part of the axial
Q40: You are reading the journal of an
Q47: Which species is an invasive species?<br>A) pika
Q60: Cellular respiration demonstrates the theme of matter
Q66: The light reactions occur in the _,
Q70: How does the sperm of an angiosperm
Q74: Which of the following statements regarding enzyme
Q88: Which of the following structures is/are used