When a scientist examined museum specimens of a particular moth species, she noticed that the variation in color was distributed as shown in the first graph. She was surprised because her data from current collections indicated the distribution of colors shown in the second graph. Which hypothesis about the cause of this shift in the range of genetic variation is the most likely to be supported by examination of the distribution of colors in a collection assembled at a time between that of the collection of the museum specimens and her current specimens? 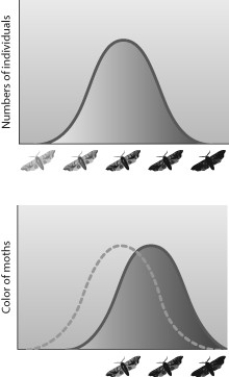
Definitions:
Impeachment Issue
The process and controversies surrounding the charging of a public official, such as the President, with wrongdoing and the potential for removing them from office.
Unconstitutional Acts
Acts or laws that are found to violate a constitution, especially the U.S. Constitution, and are therefore invalid.
Congress
The national legislative body of a country, particularly referring in the United States to the bicameral legislature that constitutes the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Land Reform
The process of redistributing or regulating land ownership, often intended to increase agricultural production or to rectify inequities in land distribution.
Q4: Which of the following lines of evidence
Q21: Which president first warned of the rising
Q21: Which of the following issues serves as
Q23: Adult stem cells have limited therapeutic potential<br>A)
Q32: All of the following mechanisms are used
Q38: The wooden box into which House members
Q39: The number of proteins in humans<br>A) is
Q53: The "big bang" that produced the universe
Q56: In a population of plants with a
Q62: The ultimate source of all new alleles