Use Figure 8.2 and the compounds labeled A, B, C, D, and E to answer the following questions.
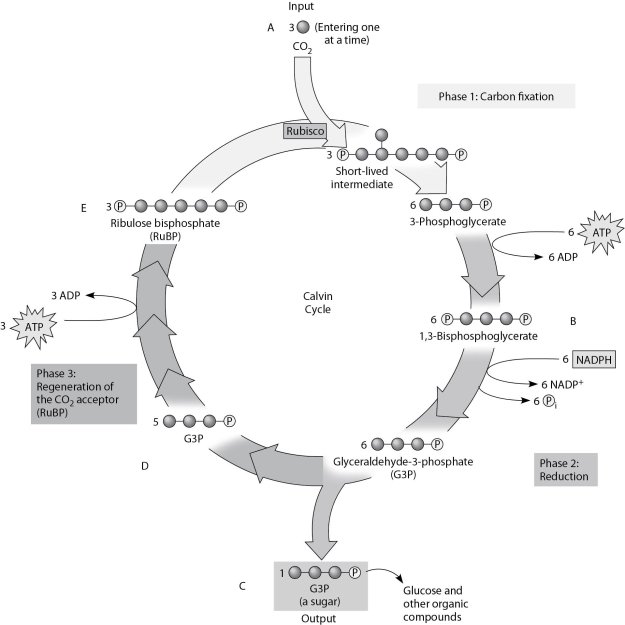 Figure 8.2
Figure 8.2
-To identify the molecule that accepts CO2, Calvin and Benson manipulated the carbon-fixation cycle by either cutting off CO2 or cutting off light from cultures of photosynthetic algae. They then measured the concentrations of various metabolites immediately following the manipulation. How would these experiments help identify the CO2 acceptor? Study Figure 8.2 to help you in determining the correct answer.
Definitions:
Friedman Test
A non-parametric statistical method for identifying treatment differences across several trials.
Sign Test
An assessment method without parametric assumptions, designed to check for differences in the median of matched data points.
Randomized Block Experiment
An experimental design that groups subjects into blocks based on certain characteristics before randomly assigning treatments within each block to reduce variation.
Interval
A range of values between two points, often used in statistics to describe the confidence levels of estimations or predictions.
Q2: Zeppo created a new rating scale designed
Q4: As most inferential statistics (e.g. ,t values,chi
Q4: Derek's proposed research study involves him engaging
Q14: What are the products of linear electron
Q15: Which of the following was NOT mentioned
Q18: Which is the easiest to assess statistically?<br>A)construct
Q18: Which of the following is NOT true
Q25: The most important difference between a census
Q29: The formula Χ<sup>2 </sup>=Σ is used to
Q55: Which of the following provides the best