 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2
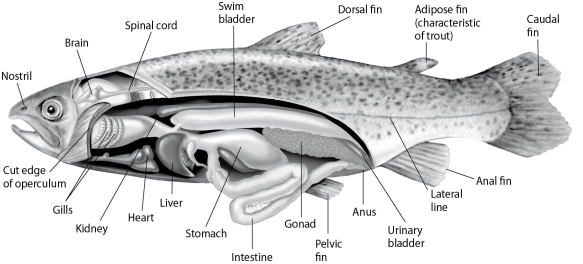
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and thus their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomus and physoclistus. The ancestral version is the physostomus version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (Figure 27.2) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistus version is more derived, and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-Rank the following fish, from most to least, in terms of the amount of energy each must use to maintain its position (depth) in the water column over the long term. 1. physoclistus fish
2) physostomus fish
3) chondrichthyan fish
Definitions:
Organized Skills
The ability to systematically arrange tasks, responsibilities, and objectives to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
Motivation
The drive or force that encourages individuals to act towards achieving a goal.
Team Performance
Refers to the level of efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity with which a group of individuals achieves shared goals.
Cross-functional Team
A cross-functional team is composed of members from different departments or specialties working together towards a common objective.
Q1: Which of the following cells transport sugars
Q1: Mycoplasmas are bacteria that lack cell walls.
Q2: Which of the following treatments would enhance
Q8: A crucial photosynthetic gene of the cyanobacterium
Q12: One explanation for the evolution of insect
Q18: Consider the thermoacidophile Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Which of
Q30: Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium must occur in populations where<br>A)
Q31: The higher the proportion of loci that
Q98: Ecologists often build models to depict the
Q101: Jaws first occurred in which extant group