The following questions refer to Figure 27.1.
In this eight-year experiment, 12 populations of E. coli, each begun from a single cell, were grown in low-glucose conditions for 20,000 generations. Each culture was introduced to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Occasionally, samples were removed from the populations, and their fitness in low-glucose conditions was tested against that of members sampled from the ancestral (common ancestor) E. coli population.
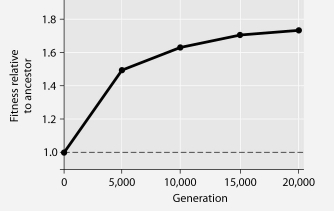
Figure 27.1
-If the experimental population of E. coli lacks an F factor or F plasmid, and if bacteriophages are excluded from the bacterial cultures, then which of these is (are) means by which beneficial mutations might be transmitted horizontally to other E. coli cells?
Definitions:
Parasympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system responsible for stimulating "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities when the body is at rest, promoting calming and a return to maintenance functions.
Central Nervous System
This refers to the complex system comprised of the brain and spinal cord, acting as the primary control center for processing and sending out nerve signals throughout the body.
Endocrine System
A collection of glands that produce hormones which regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood, among other things.
Plasticity
The brain’s special capacity for change.
Q12: Which of the following molecules contains the
Q14: Which one of the following pairs of
Q27: Which drawing in Figure 2.3 depicts an
Q27: The great apes comprise the family Hominidae,
Q47: The Hox genes came to regulate each
Q67: Which two species might be expected to
Q70: Which of the following is a defining
Q92: In which of the following taxa does
Q94: Which drawing in Figure 2.3 depicts an
Q111: Arrange the following terms from most inclusive