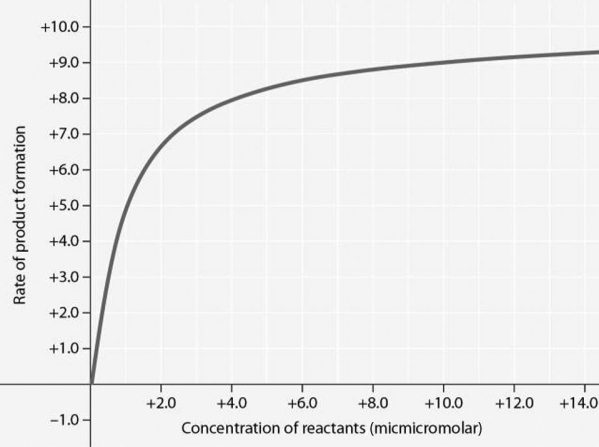
 Figure 6.2 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme held constant.
Figure 6.2 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme held constant.
-In Figure 6.2, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
Definitions:
Promoter Regions
Specific DNA sequences where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription of genes.
Operator
In genetics, a segment of DNA to which a repressor binds, controlling the expression of genes; in mathematics, a function or symbol that represents a function from a set of numbers.
Polyadenylation
That part of eukaryotic mRNA processing in which multiple adenine-containing nucleotides (a poly-A tail) are added to the 3' end of the molecule.
Prokaryotic mRNA
Messenger RNA found in prokaryotic organisms that is used to carry genetic information from DNA for protein synthesis.
Q9: P680+ is said to be the strongest
Q14: Aquatic primary productivity is most limited by
Q16: Which of the following best describes a
Q21: The cell cycle is regulated at the
Q27: Between which two genes would you expect
Q28: What is our innate appreciation of wild
Q34: How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants
Q53: Burning fossil fuels releases oxides of sulfur
Q75: Based on the figure below, which of
Q78: A noncompetitive inhibitor decreases the rate of