 Figure 5.2
Figure 5.2
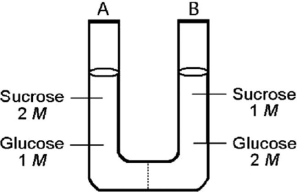
The solutions in the two arms of this U-tube (Figure 5.2) are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose. Side A is half-filled with a solution of 2 M sucrose and 1 M glucose. Side B is half-filled with 1 M sucrose and 2 M glucose. Initially, the liquid levels are equal. Refer to the figure to answer the following question(s) .
-After the system depicted in the figure reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed with respect to the concentrations of sugars?
Definitions:
Near Point
The closest distance at which an object can be seen distinctly by the eye without blurring.
Oval Window
A membrane-covered opening that leads from the middle ear to the vestibule of the inner ear, where sound waves are transmitted to the cochlea.
Ossicles
The three small bones in the middle ear called the malleus, incus, and stapes, which are essential for the transmission of sound.
Eardrum
A slim barrier dividing the external ear from the middle ear, which oscillates upon receiving sound vibrations.
Q11: The smallest cell structures that would most
Q30: Carotenoids are often found in foods that
Q33: The blood-brain barrier<br>A) filters the entry of
Q49: Which of the following describes the critical
Q52: The major role of detritivores in ecosystems
Q55: In the cells of some organisms, mitosis
Q56: A mother goat can recognize its own
Q61: Which animal cell organelle contains enzymes that
Q62: In chemiosmosis in mitochondria, protons flow from
Q66: ATP is an example of which of