What is the standard cell potential for a voltaic cell using the Pb2/Pb and Mg2/Mg half-reactions? Which metal is the cathode? Standard Reduction
Potentials (volts) in Aqueous Solution 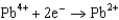 1.80
1.80 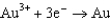 1.50
1.50 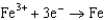 0.771
0.771 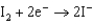 0.535
0.535 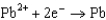 0.124
0.124 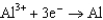 1.66
1.66 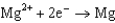 2.37
2.37 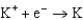 2.93
2.93
Definitions:
Salivation
The secretion of saliva in the mouth, which is often triggered by the presence or anticipation of food.
Behaviorism
A school of psychology that focuses on observable behaviors and the ways in which they're learned, rather than on feelings or thoughts.
Psychology
The science of behavior and mental processes.
Objective Science
Objective science pertains to the study of the natural world based on observable, measurable evidence, free from personal biases or emotions.
Q52: The following reaction is called the "super
Q62: All elements with Z <font face="symbol"></font> 83
Q65: Plants convert nitrogen into ammonia. This biological
Q81: Which statement about this concentration cell is
Q88: A patient is injected with a 5.0
Q100: In DNA, the base adenine can pair
Q127: When an atom of uranium-235 captures a
Q157: The capacity of a battery usually is
Q161: The thermite reaction, shown below, is very
Q165: The entropy change in the surroundings (<font