Solid mercury(II) oxide decomposes when heated to produce liquid mercury and oxygen. 2HgO(s) 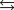 2Hg(l) O2(g)
2Hg(l) O2(g)
An amount of mercury(II) oxide is placed in a vessel at a particular temperature and allowed to reach equilibrium. How could the amount of liquid mercury in the vessel be increased?
I. adding more mercury(II) oxide
II. removing some oxygen
III. increasing the volume of the vessel
Definitions:
Adverse Selection
A situation where asymmetric information results in high-risk individuals being more likely to select into or remain in a contract designed for low-risk individuals, affecting insurance markets and other transactional relationships.
Asymmetric Information
A situation in which one party to a transaction has more or superior information compared to another.
Moral Hazard
The situation where one party is more likely to take risks because they do not bear the full consequences of those risks.
Hidden Action
A situation in contract theory and economics where one party's action is not observed or cannot be monitored by another, potentially leading to moral hazard.
Q1: Identify the solid that has a high
Q5: Which of the following is not a
Q29: The equilibrium constants for the two reactions
Q61: Which one of the following salts forms
Q64: Magnesium sulfate can be obtained at a
Q72: What type of motion is depicted in
Q85: Indicate which aqueous solution has the slowest
Q140: Describe how the data obtained by a
Q182: The prediction of linearity in a van
Q186: The symbol <font face="symbol"></font><font face="symbol"></font> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3835/.jpg"