Automobile air bags inflate during a crash or sudden stop by the rapid generation of nitrogen gas from sodium azide. 2NaN3(s)  2Na(s)
2Na(s) 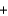 3N2(g)
3N2(g)
How many moles of sodium azide are needed to produce sufficient nitrogen to fill a 50.0 L air bag to a pressure of 1.25 atm at 25°C?
Definitions:
Poisson Arrivals
A statistical distribution that models the number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space, assuming independence among arrivals.
FIFO Discipline
First In, First Out Discipline is a queue management principle where the first item or task to arrive is the first to be processed or completed.
Normal Curve
A bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of many types of data where most of the occurrences take place around the average.
M/M/1 Model
is a type of queueing model used in operations research to describe systems with a single server, where arrivals are determined by a Poisson process and service times have an exponential distribution.
Q8: What pressure will be measured (in Pa)
Q14: Which statement about the quantum numbers that
Q19: A typical adult body contains about 6.0
Q34: Which of the following has a central
Q65: Which of the transitions in the following
Q68: Which statement about the following chemical reaction
Q78: Which statement below regarding the various heat
Q101: How many chlorine atoms are there in
Q125: Lead is the least toxic metal ion
Q140: The local molecular geometry and the hybridization