Use the following information to determine the standard enthalpy change when 1 mol of PbO(s) is formed from lead metal and oxygen gas. PbO(s) 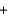 C(graphite)
C(graphite)  Pb(s)
Pb(s) 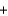 CO(g) H
CO(g) H  107 kJ
107 kJ
2C(graphite) 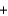 O2(g)
O2(g)  2CO(g) H 222 kJ
2CO(g) H 222 kJ
Definitions:
Mean
The average of a set of numbers, calculated by adding them together and dividing by the count of numbers.
Sample Variance
A measure of variability within a sample dataset, calculated by taking the sum of squared differences from the mean divided by the number of observations minus one.
Standard Deviation
A statistics metric that quantifies the variation or dispersion of a set of values.
Sample Mean
The average value of a sample, calculated by summing all the observations and dividing by the number of observations in the sample.
Q6: Which of the following elements would you
Q7: Which of the following fuels has the
Q11: Three bulbs are connected as shown in
Q22: Which of the following is a correct
Q28: Which one of the following is an
Q48: The National Primary Drinking Water Regulations limit
Q53: In an experiment, 30.0 g of metal
Q67: A pot of water is heated with
Q110: When the principle quantum number <font face="symbol"></font>
Q132: Draw the Lewis structure for the carbonate