The orbits of the planets can be modeled easily by assuming i). that the sun is a perfect sphere and ii). that each planet is influenced only by the gravitational field of the sun (that is, each planet is unperturbed by gravitational forces from other planets, distant stars, etc.). According to Newton's (classical) theory of gravity, these assumptions result in elliptical planetary orbits with the sun at one focus. That is, the orbit can be described by the polar equation 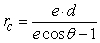 . However, according to Einstein's (relativistic) theory of gravitation, the orbits are more accurately described by
. However, according to Einstein's (relativistic) theory of gravitation, the orbits are more accurately described by 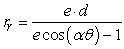 , where
, where 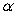 is a constant such that
is a constant such that 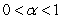 . Describe how the inclusion of the factor
. Describe how the inclusion of the factor 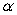 affects the orbit. That is, compare the classical orbit to the relativistic orbit. How do they differ? Draw figures that summarize the differences in the classical and relativistic orbits.
affects the orbit. That is, compare the classical orbit to the relativistic orbit. How do they differ? Draw figures that summarize the differences in the classical and relativistic orbits.
Definitions:
Secondary Growth
Growth produced by lateral meristems, thickening the roots and shoots of woody plants.
Vascular Cambium
The vascular cambium is a layer of dividing cells in plants, responsible for producing new phloem and xylem, contributing to the plant's secondary growth.
Bark
The outer protective layer of a tree's trunk, branches, and roots, comprised of dead cells.
Organelles
Specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions necessary for the cell's life, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and the Golgi apparatus.
Q1: Is the following differential equation separable or
Q8: Is the following differential equation separable or
Q21: Find the area of the indicated region.
Q25: Identify the equilibrium solutions for <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2342/.jpg"
Q31: Find the derivative <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2342/.jpg" alt="Find the
Q54: The table shows the velocity of a
Q58: What mass of phosphoric acid (H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub>, 98.0
Q102: Find the area enclosed by the given
Q108: Carbon monoxide is used in refining iron
Q117: What is the correct symbol for a