Suppose that a car can come to rest from 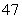 mph in
mph in 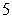 seconds. Assuming a constant (negative) acceleration, find the acceleration (in miles per second squared) of the car and find the distance traveled by the car during the
seconds. Assuming a constant (negative) acceleration, find the acceleration (in miles per second squared) of the car and find the distance traveled by the car during the 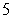 seconds (i.e., the stopping distance) .
seconds (i.e., the stopping distance) .
Definitions:
Unsafe Work Behaviours
Actions or practices by employees that disregard safety protocols and increase the risk of accidents or injuries.
Internal Forces
Dynamics within an organization or system that drive changes or influence its operations without external intervention.
External Locus
Refers to the belief that one's success or failure is due to external forces beyond one's control.
High Self-monitor
An individual who is highly attentive to societal cues and adapts their behavior accordingly to fit in different social situations.
Q20: Use a table of integrals to find
Q30: Set up the integral for the surface
Q43: Evaluate the integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2342/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q43: Determine whether <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2342/.jpg" alt="Determine whether
Q44: Find the derivative of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2342/.jpg" alt="Find
Q53: Use summation rules to compute the sum.
Q61: Find the gradient field corresponding to <img
Q89: Write the expression as a single integral.
Q107: Find the mean of the random variable
Q142: Find a value of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2342/.jpg" alt="Find