Convert 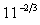 into fractional or root form.
into fractional or root form.
Definitions:
Voting Paradox
is a situation in social choice theory where collective preferences can be cyclic (A is preferred to B, B is preferred to C, and C is preferred to A), despite the individual preferences being consistent.
Majority-Rule Voting
A decision-making process where the option that receives more than half of the votes is chosen, commonly used in democratic systems and organizations.
Voting Paradox
A situation in social choice theory where collective preferences can be cyclic (i.e., not transitive), even if the preferences of individual voters are not, leading to a lack of consistent aggregation of individual preferences into a coherent group order.
Impossibility Theorem
A principle, also known as Arrow's impossibility theorem, stating that it is impossible to devise a social welfare function that fairly ranks societal preferences in the presence of three or more options.
Q2: Disruptive conflict in groups or teams is
Q3: The process of communication that aims at
Q5: Ethos is proof based on logic and
Q6: Find an equation of the line with
Q20: Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to determine
Q22: Assuming an attentive posture, holding eye contact,
Q30: Research has shown that babies in dysfunctional
Q32: Reframing dialectical tensions involves seeing the tensions
Q43: _ involves curiosity, rather than judgment, as
Q87: Find a vector perpendicular to the given