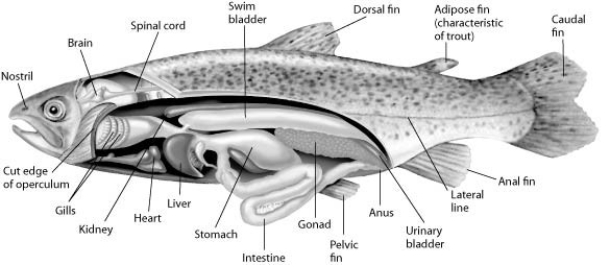
 Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and, thus, their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the oesophagus via a short tube (see the figure) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching". The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the oesophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and, thus, their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the oesophagus via a short tube (see the figure) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching". The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the oesophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-If a ray-finned fish is to both hover (remain stationary) in the water column and ventilate its gills effectively, then what other structure besides its swim bladder will it use?
Definitions:
Interneurons
Neurons that transmit signals between sensory and motor neurons, playing a critical role in the central nervous system by integrating sensory input and motor output.
Interoceptors
Sensory receptors located inside the body that provide information about the internal environment, such as pH levels, temperature, and other internal states.
Blood PH
A measure of the acidity or alkalinity of blood, normally maintained within a narrow range around a neutral pH of 7.4.
Mechanoreceptors
Sensory receptors in the body that respond to mechanical pressure or distortion, playing an essential role in the senses of touch and hearing.
Q3: In the figure, meiosis is most likely
Q12: Theoretically, P. bursaria can obtain zoochlorellae either
Q14: If a long-day plant has a critical
Q16: Generally, epithelial cell layers are responsible for
Q32: Imagine that you wanted to know if
Q35: Chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) are born in
Q37: Refer to the study by Poulsen et
Q42: Which of the following experimental procedures would
Q46: You may have observed plants rotate towards
Q48: The metabolic breakdown of specialised brown fat