In this eight-year experiment, 12 populations of E. coli, each begun from a single cell, were grown in low-glucose conditions for 20,000 generations. Each culture was introduced to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Occasionally, samples were removed from the populations, and their fitness in low-glucose conditions was tested against that of members sampled from the ancestral (common ancestor) E. coli population. 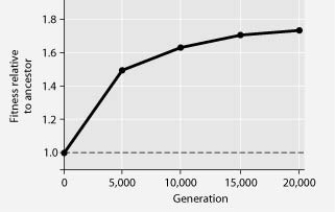
-
The cells in the 12 cell lines grown in low-glucose conditions showed the effects of which of the following processes?
Definitions:
Directional Selection
A form of natural selection where one extreme phenotype is favored over others, causing the allele frequency to shift in one direction.
Extreme Phenotype
The manifestation of traits at the extreme endpoints of a genetic expression spectrum.
Inbreeding
The breeding of closely related individuals, which increases the risk of offspring inheriting genetic defects.
Nonrandom Mating
A mating pattern in which individuals choose partners based on particular traits, leading to non-random distribution of alleles in the population.
Q14: For several decades now, amphibian species worldwide
Q16: About 450 million years ago, the terrestrial
Q16: Beetle pollinators of a particular plant are
Q16: Which tree depicts the closest relationship between
Q19: Currently, cacao is harvested by cutting the
Q34: Which factor most likely caused animals and
Q35: Normally, the clown fish readily swims among
Q45: When Cuvier considered the fossils found in
Q46: Entrepreneurs attempted, but failed, to harvest nuts
Q72: Planarians lack dedicated respiratory and circulatory systems.