In the oceans on either side of the Isthmus of Panama are 30 species of snapping shrimp; some are shallow-water species, others are adapted to deep water. There are 15 species on the Pacific side and 15 different species on the Atlantic side. The Isthmus of Panama started rising about 10 million years ago. The oceans were completely separated by the isthmus about 3 million years ago.
In the figure, the isthmus separates the Pacific Ocean on the left (side A) from the Atlantic Ocean on the right (side B) . The seawater on either side of the isthmus is separated into five depth habitats (1-5) , with 1 being the shallowest.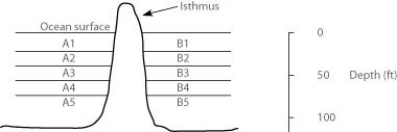
-
Which of these habitats is likely to harbour the most recently diverged species?
Which of these habitats is likely to harbour the most recently diverged species?
Definitions:
Occipital Stimulus
A stimulus that targets the occipital lobe of the brain, primarily involved in visual processing.
Proximal Stimulus
The physical energy from a stimulus that directly interacts with sensory receptors.
Agnosias
A class of neurological disorders marked by the inability to recognize objects, people, sounds, shapes, or smells while other sensory functions remain intact.
Aphasias
Language disorders caused by damage to the brain that affect speaking, understanding, reading, and writing.
Q8: Which of the five common ancestors, labelled
Q16: Which of the following statements correctly describes
Q18: <br>How many of these species probably have
Q30: Which statement describes unity within a species?<br>A)
Q47: What is the significance of measuring fruit
Q50: Assuming that each of these possesses a
Q51: Why are fossils considered to be an
Q53: RNA viruses require their own supply of
Q70: In the figure, which number represents an
Q75: Upon closer inspection of the leaves of